- Home
- Dr Sultan Linjawi
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes
Prediabetes
Gestational Diabetes
- Diabetes Information
- Testimonials
All fruits are not the same in terms of sugar, carbs and calories. So what is the best fruit for diabetics?

It is well known that eating a varied diet of plenty of fruit and veg is important for our health. Most of us don’t eat enough fruit and veg either. For people with Type 2 diabetes, it can sometimes be a tricky balance between aiming to eat enough fruit and veg, but avoiding a huge rise in blood glucose levels.
If you are someone with Type 2 diabetes, it is important for you to have a better understanding of what types of fruit will have the greatest impact on your blood glucose levels.
What is glucose and how does it affect blood glucose levels?
Glucose provides energy to our body.
The food that we eat is broken down into smaller components, or macro- and micronutrients. There are three macronutrients; carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Carbohydrates are an important source of energy for our bodies, and there are simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates. Glucose is a type of simple carbohydrate and has a direct impact on our blood glucose levels. Micronutrients is another name referring to vitamins and minerals.
When we eat fruit, for example a banana, it is broken down into glucose. This glucose is then released into our blood where it can travel around our body, providing it with energy. This includes all of our muscles, heart, and brain. They all need energy!
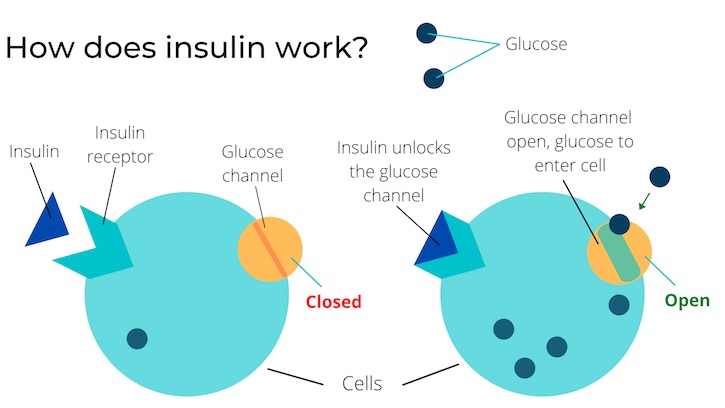
The way that glucose gets into our cells, is through the action of insulin.
What is insulin and how does it work?
Insulin is a small naturally occuring chemical in our body. Insulin acts like a key, whose purpose is to bind to a receptor (the lock) on the surface of fat and muscle cells. When insulin binds to the insulin receptor, it opens a glucose channel to allow glucose to enter those cells. This process is how we get glucose from our blood stream (after it has been broken down from the food we eat) into the cells of our body, to provide our body with energy.
Importance of eating fruit
Fruit contains a variety of vitamins and minerals, which are important for our health. Fruit is also a quick and easy snack.
When choosing a snack, choosing a piece of fruit over a packet of chips, is a better choice as fruit has all the other important nutrients in it that our bodies need.
If you are someone with diabetes, it is important to consider the type of fruit you are choosing to snack on. As Dr Sultan has mentioned, some fruit will affect your blood glucose levels more than others. And before you realise, your blood glucose levels might be quite high, resulting in hyperglycaemia.
When choosing a health snack, like some fruit, you may want to consider choosing a small handful of strawberries or a small banana instead of a large banana.
The impact of fruit on blood glucose levels
Blood glucose levels, sometimes called blood sugar, will change depending on what we eat. When we eat food and it has been broken down and digested, our body will release the glucose into the blood stream to provide our body with energy.
For people with diabetes, it is important to be mindful of the amount of carbohydrate food that you are eating every day. Being aware of your carbohydrate intake, can ensure that you are managing the condition well.
Improving your carbohydrate awareness
When you are prediabetes or type 1 or type 2 diabetes, it is important to be aware of what foods contain carbohydrates. Some foods contain very little carbohydrate, for example broccoli, avocado, beef, chicken. Foods like bread, milk, corn, and bananas all contain carbohydrates.
15g carbohydrate = 1 carbohydrate portion
Understanding carbohydrate portions is important for managing blood glucose levels and can be used as a strategy for weight reduction and maintenance.
One serving of carbohydrate is measured as 15 grams. A food that contains 15 grams of carbohydrate is also called “one portion of carbohydrate” or simply “one portion.” You can use portions of carbohydrates to help with your carb counting.
Your doctor or dietitian may set you an amount of allowable portions of carbohydrates you can consume in a day. This will depend on your age, if you’re trying to lose weight, and your activity levels. Generally speaking, Dr Sultan recommends 10-12 portions for men and 6-9 portions for women.
What fruit is lower in carbohydrates?
In the video, Dr Sultan mentions that strawberries are lower in carbohydrate compared to bananas. But what other fruits are low in carbs?
Some examples of fruits with very little carbs include:
- avocado
- apricots
- nectarines
- grapefruit
- orange
- lemon and lime
- blueberries
- blackberries
- strawberries
- passionfruit
- guava
- pineapple

Low carbohydrate fruit portions
The below table can help you compare different portions of low carbohydrate fruits.
| Low carb fruit | Small | Medium | Large |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nectarine | 95g whole (87g edible portion) 7g CHO 1/2 portion |
150g whole (138g edible portion) 11g CHO 2/3 portion |
200g whole (184g edible portion) 15g CHO 1 portion |
| Blackberries | 1/2 punnet (8 berries) 5g CHO 1/3 portion |
125g punnet (16 berries) 10g CHO 2/3 portion |
150g punnet (19 berries) 17g CHO 1 portion |
| Blueberries | 1/2 punnet 7g CHO 1/2 portion |
125g punnet 14g CHO 1 portion |
150g punnet 17g CHO 1 1/4 portion |
| Kiwi fruit | 80g whole (60g edible portion) 6g CHO 1/3 portion |
100g whole (75g edible portion) 7g CHO 1/2 portion |
150g whole (120g edible portion) 11g CHO 2/3 portion |
| Orange | 155g whole (60g edible portion) 9.5g CHO 2/3 portion |
235g whole (165g edible portion) 14g CHO 1 portion |
390g whole (286g edible portion) 30g CHO 2 portion |
| Passionfruit | 55g whole (22g edible portion) 1g CHO 0 portion |
75g whole (32g edible portion) 2g CHO 0 portion |
100g whole (42g edible portion) 11g CHO 1/4 portion |
| Plum | 75g whole (71g edible portion) 5g CHO 1/3 portion |
95g whole (90g edible portion) 6g CHO 1/2 portion |
155g whole (148g edible portion) 10g CHO 2/3 portion |
| Peach | 80g whole (76g edible portion) 6g CHO 1/3 portion |
165g whole (150g edible portion) 12g CHO 1 portion |
240g whole (216g edible portion) 17g CHO 1 1/4 portion |
| Strawberries | 1/2 punnet (125g) 5g CHO 1/3 portion |
1 punnet (250g) 10g CHO 2/3 portion |
2 punnets (500g) 19g CHO 1 1/3 portion |
Why is diet important in diabetes?
There are many factors that can affect how well diabetes is controlled. Many of these factors relate to and are controlled by the person who has diabetes. These factors can include how much food and drink has been consumed, how frequently blood glucose levels are being monitored, exercise and physical activity levels, and consistency with taking any prescribed medications. Even small changes can influence and affect blood glucose control, for example exercising 3 days a week instead of 2 days.
When it comes to food, eating a consistent amount of food every day and taking any medications as directed, can greatly improve blood glucose control. Doing this can help to keep blood glucose levels consistent, rather than having big highs and lows. Consistent blood glucose levels in the healthy range can reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, including heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Eating regular meals can also help with weight loss!
If you’re struggling to stay motivated and want to learn more about what you can do to get on track with your diabetes management, you can join our personalised 12-week type 2 diabetes program. There are so many great videos where Dr Sultan explains complex topics in simple terms that everyone can understand.
Important things to remember if you have diabetes
- Choose whole fruit over dried fruit or fruit juice
- Don't eat all your servings of fruit at once - spread the fruit you eat evenly across the day
- Fruit contains carbohydrates and can impact your blood sugar readings - you may need to check your blood glucose levels after you eat fruit
- The size of the fruit can alter the amount of carbohydrate dramatically - choosing smaller fruits will reduce your carbohydrate intake
Diabetes and Diet Articles - What do I need to know?
Diet, and what you eat, plays an important role in diabetes management. Your diet is also classified as a modifiable risk factor in diabetes. Making changes to your diet can even play an important role in reducing the risk of developing diabetes related complications.
Follow the links below to learn more about diet in diabetes.
Diabetes diet: what should I eat if I have type 2 diabetes?

Making healthy food choices is important in diabetes treatment. In ‘Diabetes diet: what should I eat if I have type 2 diabetes,’ we have outlined 7 important changes you can make to you diet.
How to reduce carbs in your diet

There are so many helpful tips in this article! We cover some clever ways to reduce the carbohydrate content of the meals you are eating, without losing any flavour.
Should I follow a ‘low carb’ diet if I have diabetes?

There are so many helpful tips in this article! We cover some clever ways to reduce the carbohydrate content of the meals you are eating, without losing any flavour.
Diabetes diet. Why is it not more simple?

The link between diabetes and diet isn’t so simple. Food and nutrition do play a role when developing diabetes. But what does the evidence say?
The “Diabetic Diet”: When did it begin and how has it changed?

This article is great for those who like a little history! The article talks about how the treatment of diabetes has changed over the years, starting from 1500 BCE!
Yo-Yo Dieting – More serious than just regaining weight!

Yo-Yo dieting can be harmful to your health. A correlation has been found with yo-yo dieting and heart disease! You can read about the Framingham Heart Study in this article.
4 easy diet and exercise steps!

Looking for some really quick tips on how to make simple changes to your diet and exercise? We have them here and it involves the whole family!
How Can People Eat Junk And Not Gain Weight?

Remember: thin doesn’t necessarily equal healthy. And this was confirmed in a new report which showed that a poor diet is one of the highest contributing factors to chronic disease in Australia, second only to smoking!
Why Do We Eat When We Are Not Hungry?

Typically, people who are tuned in to their hunger cues are able to stop eating when they are satisfied and won’t eat again until they become hungry. This is referred to as intuitive eating. But even intuitive eaters will sometimes override their fullness signals for certain triggers.
When our food choice isn't just about food

Have you ever felt like your food preference or portion sizes were almost out of your control? It is possible that in some way they are. The difficult thing is eating can be driven by our mind instead of being a behaviour to reduce physical feelings of hunger and to stay alive and well.
How to treat a hypo without spinning your sugars into the twenties!

While the best way to manage a hypo is to prevent one happening in the first place, preparing for a hypo is the next best thing. As soon as your BGLs drop below 4mmol/L (72mg/dL), you need to act, as an untreated hypo can turn into a medical emergency very quickly.
Video Transcript
Now we all know it is important to eat fruit and we are often told that we need to increase our fruit consumption and if you are someone who really enjoys eating fruit likes eating fruit I think this is something that you probably need to listen to.
Whilst fruit is an excellent source of energy and vitamins and nutrients not all fruit is the same and some fruit can actually not be so good for us.
And so just on that note I would like to start with thinking about a piece of fruit like a banana.
The amount of carbohydrate and in effect the amount of sugar that is in the banana is the equivalent of about this many strawberries. So clearly all fruit is not the same.
And some fruits may be better, particularly if you have diabetes or if you are worrying about your weight, than others.
So you will see often athletes will consume bananas when they are competing, they will rarely have strawberries, because it doesn't have enough energy.
But let's say you really want a banana and that every morning you wake up and have a banana and you think that is really important, well then you can make a simple choice rather than stopping bananas completely, maybe it is just about choosing a banana that is smaller or having half a banana so that you still get the taste, without all of the calories, without all of the sugar, and without all of the potential effects that this will have on your body.
If you found this video helpful then please subscribe to the channel so that I can keep you up to date as all the new videos come online.

