- Home
- Dr Sultan Linjawi
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes
Prediabetes
Gestational Diabetes
- Diabetes Information
- Testimonials
Tools and tricks to help manage gestational diabetes

Tools for gestational diabetes
We have developed some tools that can help you to monitor your progress!
These tools can help to monitor your haemoglobin A1c (Hb A1c), your blood glucose levels (BGLs), and body mass index (BMI).
These tools are all used to monitor how someone with diabetes is managing their blood glucose levels and their weight. By maintaining blood glucose levels and weight in a healthy range, can reduce the risk of complications.
Gestational Diabetes Content |
|---|
| Gestational Diabetes Program |
| Overview |
| Risk Factors |
| Symptoms |
| Diagnosis |
| Complications |
| Treatment |
| Diet |
| Monitoring |
| Tools |
| Mental Health |
| Prevention |
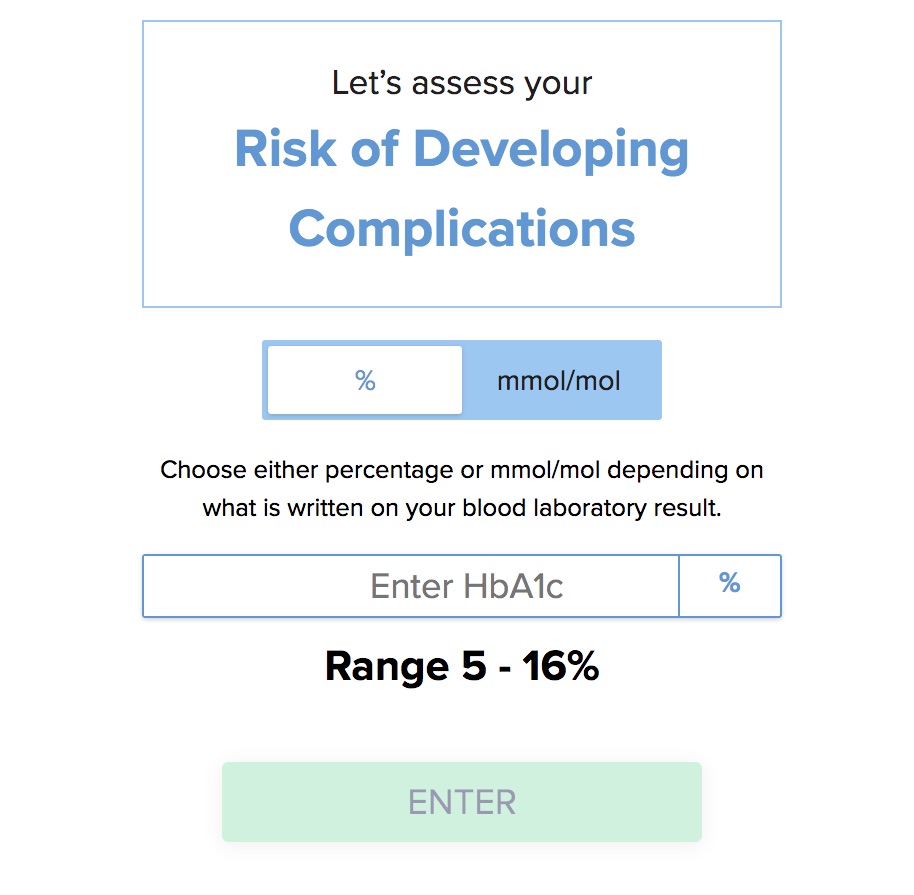
Haemoglobin (Hb A1c) Calculator
The Hb A1c is blood test that provides a method of monitoring the blood glucose levels of a person with diabetes, over the previous 3 months. It does this by providing an average of what your blood glucose levels are.
The Hb A1c can be used to work out the estimated average glucose (eAG) level using a complex mathematical model. The estimated Average Glucose (eAG) is a way to show patients what their Hb A1c results (shown as a percentage) are using the same units (mg/L or mmol/L) that they're more familiar with when monitoring their blood glucose levels.
For more information about Hb A1c, watch the video with Dr Sultan on our haemoglobin A1c tool page.
We also have more information about the Hb A1c test. Find the articles below:
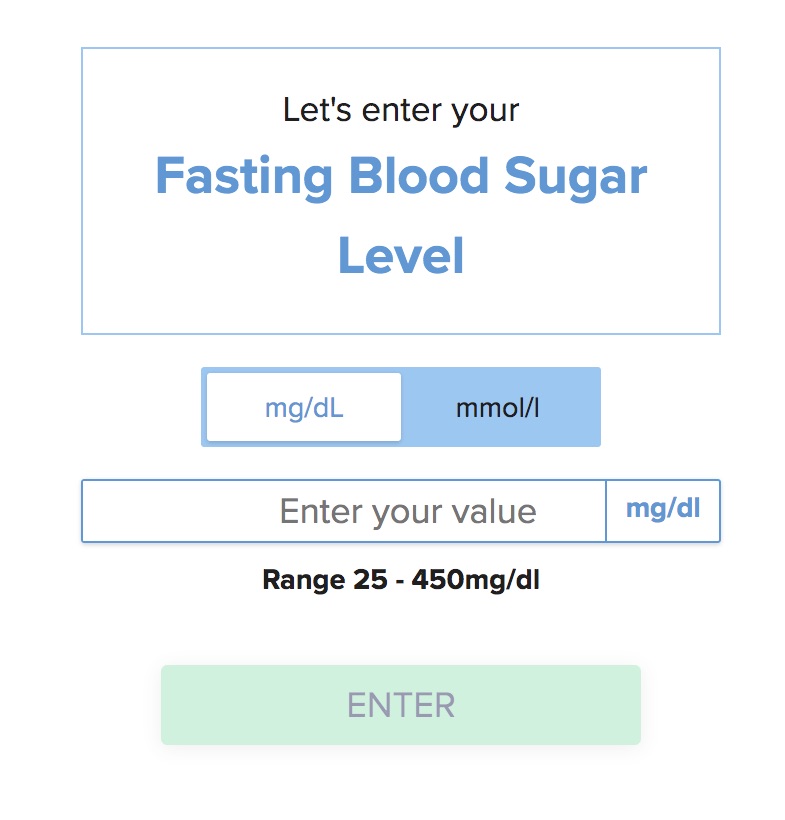
Fasting Blood Glucose Calculator
The fasting glucose level is an important measurement to define whether a person has diabetes or borderline diabetes (also called prediabetes).
The fasting glucose level also provides information into how well someone with diabetes is managing and help identify the most suitable diabetes treatments.
You can use the tool to help you to better understand how your blood glucose levels are going.
For more information about fasting blood glucose, watch the video with Dr Sultan on our fasting blood glucose tool page.
Try the tool below!
Body Mass Index (BMI) Calculator
The BMI (Body Mass Index) is a simple equation to compare a person's weight with their height. It does not take into account difference in body shape or how much muscle a person has compared to fatty tissue.
The BMI does correlate with the risk of heart disease, many cancers, and even death. Is therefore used by doctors and health professionals to work out "an ideal body weight" to help people on their life journey.
For more information about BMI, watch the video with Dr Sultan on our body mass index tool page.
What should I do next?
If you are at risk of developing gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy), you can prevent complications of gestational diabetes by making changes now. These complications can impact both you and your baby. Not only during the pregnancy, but also further down the line (for mum; after pregnancy, and for baby; into adulthood). It is recommended for all pregnant women to be tested for gestational diabetes at 24-28 weeks. If you are at a much higher risk, you should request to be tested for diabetes before pregnancy, at 12 weeks’ gestation, and again at 24-28 weeks’.
Once you learn what your gestational diabetes status is, the next most important step is to become educated. You can join the Gestational Diabetes Program to help you learn how to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes. The program is personalised, giving you more of the content that you want. The program also helps you to stay motivated and teaches you what changes you need to make.
What should I do next?
If you experience any symptoms of gestational diabetes or you have risk factors for developing gestational diabetes, it is important to be tested at 24-28 weeks gestation. Some people are at higher risk than others. If you are 25 years or older or have other risk factors for diabetes, you may require testing earlier in pregnancy. By diagnosing and treating gestational diabetes, it means you can decrease the risk of developing or delay any further health complications of gestational diabetes. These complications can affect both you and your child later in life, for example you are both at risk of developing type 2 diabetes. It is important to know that diagnosing diabetes should not rely solely on using a Hb A1c test.
Once you learn what your gestational diabetes status is, or if you already have gestational diabetes, the next most important step is to become educated. You can join the Gestational Diabetes Program to help you learn how to manage gestational diabetes and improve health outcomes for you and your child. The program is personalised and tailored, giving you more of the content that you want. The program also helps you to stay motivated and teaches you what changes you need to make.
Interested in more information on gestational diabetes and diabetes in pregnancy?
Follow the links below to learn more about gestational diabetes.